|
|
| (28 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | __NOTOC__ | | __NOTOC__ |
| − | <div class="left-column-contentinner"> | + | <div class="methodpage-content"> |
| − | <div class=teaser-text>[[File:Attitude.png | right | 200px]]A shift in the attitude (or position or mindset) of the teacher or educator plays an important role. Enabling rather than controlling, strengthening rather than emphasizing on deficits, cooperating rather than delivering content, such an attitude is a success condition for competency-centered learning.</div> | + | <div class=teaser-text><div style="background: #eee; float: left; padding: 0px 5px 0px 5px; margin-right: 5px;"><i class="fas fa-arrow-left"> </i> [[Before]]</div>[[File:Attitude.png | right | 200px|link=The Facilitation Mindset]]A shift in the attitude (or position or mindset) of the teacher or educator plays an important role. Enabling rather than controlling, strengthening rather than emphasizing deficits, cooperating rather than delivering content. Such attitudes are a condition for success for competency-centered learning. |
| | + | </div> |
| | | | |
| | ==Facilitators with a holistic attitude...== | | ==Facilitators with a holistic attitude...== |
| | *Are empathic and try to understand the feelings and needs of their learners. | | *Are empathic and try to understand the feelings and needs of their learners. |
| | *Strengthen learners' independence and believe in their existing abilities and potentials. | | *Strengthen learners' independence and believe in their existing abilities and potentials. |
| − | *Strengthen learners abilities to solve problems and approach a solution. | + | *Strengthen learners abilities to solve problems and approach solutions. |
| − | *Pay attention to their relationship with learners (relationship as partnership), they don’t only focus on the content | + | *Pay attention to their relationship with learners (relationship as partnership), not only focusing on content |
| | *Are open to dealing with different opinions and conflicts resulting from them in a constructive way. | | *Are open to dealing with different opinions and conflicts resulting from them in a constructive way. |
| − | *Are interested in their self-development as facilitators. | + | *Are interested in their self-development as facilitators |
| | + | * Are using tools, methodology and technology in order to continuously improve the learning experience |
| | | | |
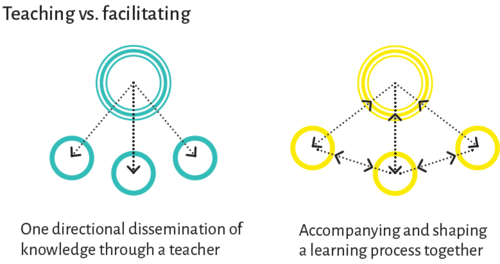
| | [[File:Teaching-facilitating.png | center| 500px]] | | [[File:Teaching-facilitating.png | center| 500px]] |
| Line 15: |
Line 17: |
| | <hr class=boldline> | | <hr class=boldline> |
| | | | |
| − | ==Articles, Checklists and Methods==
| |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-expanded" data-expandtext="Read more">
| |
| − | <div class=teaser-box>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===[[Addressing Self-responsibility]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left ]]Due to our goal of empowerment, it is logical to share as much power as possible and to prepare participants for acting powerful. Therefore we include in a first step our participants as partners and they become responsible for their learning outcome.
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <div class=teaser-box>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===[[Competencies for Educators]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left ]]The key persons (beyond the learners) for achieving qualitative learning outcome are the facilitators. Every facilitator has competencies equipping them for this task and every facilitator team is completing the required set of competencies. Therefore, no competency-centered learning without looking from a competency-centered perspective on the quality of facilitators.
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <!--
| |
| | <div class=teaser-box> | | <div class=teaser-box> |
| | + | ===Articles, Checklists and Methods=== |
| | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-expanded" data-expandtext="+ Read more" data-collapsetext="- Collapse"> |
| | | | |
| − | ===[[Focusing on self-learning strategies]]=== | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Competencies for Educators]]<br> |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left ]]Help learners in becoming independent and capable to find solutions for their challenges. Allow them to practice, to feel successes and to make mistakes. | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Constructive Relation]]<br> |
| − | </div> | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Directing and Coaching]]<br> |
| − | -->
| + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Digital Natives, Digital Learners]]<br> |
| − | <div class=teaser-box> | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Diversity as a Learning Culture]]<br> |
| − | | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Empathy]]<br> |
| − | ===[[Resource Orientation]]===
| + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Facilitation]]<br> |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left ]]In citizenship education the impact of a training or seminar approves in practice - often far long after our work as facilitators is done. When participants need to take the next steps into practice independently from us, we could strengthen their self-esteem and trust in their already existing knowledge and skills. This idea of resource orientation is contrary to the approach of deficit orientation in trainings. | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Resource Orientation]]<br> |
| − | </div> | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Learning to Learn]]<br> |
| − | | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Solution Orientation]]<br> |
| − | | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Self-Development of Educators]]<br> |
| − | <div class=teaser-box> | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[There is no Digital Didactics]]<br> |
| − | | |
| − | ===[[Solution Orientation]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left ]]A common approach in pedagogics is to concentrate on helping people finding solutions not based on their problems but rather on increasing their abilities, for reflecting “solutions to problematic patterns in thought and behaviour - and finding solutions dialogically."
| |
| − | </div> | |
| − | <div class=teaser-box> | |
| − | ===[[Constructive Relation]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left ]]Without any question, personal understanding between facilitators and participants may support learning. Such a relationship can help people to find a common language, but inspiring and motivating others involves more than addressing our participants' hearts. We have to address their minds as well. So before we form deep relationships with our students and participants, it is helpful to reflect on the situation.
| |
| − | </div> | |
| − | <div class="teaser-box"> | |
| − | | |
| − | ===[[Empathy]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left ]]Empathy is a human quality that helps people to understand, to show authentic reactions or to mobilize their capacities. It's the ability to build a trustful relationship, a skill and a precondition for the participative and respectful facilitation of groups. | |
| − | </div> | |
| − | | |
| − | <div class="teaser-box"> | |
| − | | |
| − | ===[[Self Development]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left ]]Training, teaching or youth work require specific competencies of facilitators and can be perceived as well as a learning field for facilitators. We introduce two materials - a competency framework and a learning portfolio for facilitators. | |
| − | </div> | |
| − | | |
| − | <div class="teaser-box"> | |
| − | ===[[Checklist: My Leadership Style]]===
| |
| − | [[File:check.png | left ]]As a facilitator you take on responsibility in a leading role. Different people have different styles to deal with this. Although facilitating in an empowering way means applying your approach to the needs of the target group, this can imply many different things. What does it mean for you? | |
| − | </div> | |
| − | | |
| − | <div class="teaser-box"> | |
| | | | |
| − | ===[[Checklist: Relation to Participants]]=== | + | <i class="fas fa-cog"></i> [[Constructive Feedback]]<br> |
| − | [[File:check.png | left ]]Empowerment is a process that requires eye-level cooperation between facilitator and learners. When the boundaries between facilitator and participants become more fluid, this can present a challenge to modern facilitators. How would you like to define yourself in relation to your participants.
| |
| − | </div> | |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="teaser-box"> | + | <i class="far fa-check-square"></i> [[Checklist: My Leadership Style]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="far fa-check-square"></i> [[Checklist: Relation to Participants]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="far fa-check-square"></i> [[Checklist: Your Attitude Towards Diverse Participants ]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="far fa-check-square"></i> [[Checklist: My learning goals]] |
| | | | |
| − | ===[[Checklist: Your Attitude Towards Diverse Participants ]]===
| |
| − | [[File:check.png | left ]]How do you deal with diversity in your group? A self-assessment.
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <div class="teaser-box">
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===[[Directing and Coaching]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left ]]Two main approaches of guiding constructive conversation are available for facilitators. Advice as an active proposal and coaching as a method that builds a setting in which learners come up with solutions to their challenges on their own.
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="teaser-box">
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===[[Constructive Feedback]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Method.png| left]]Feedback is a method that was developed to improve the quality of interpersonal communication, in terms of relevance (giving relevant information) as well of moral quality (showing interpersonal respect). As outside perceptions are sometimes different to internal perceptions, it is a useful tool for gaining insight on how the own action, skills and communication are perceived through other people.
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| − | | + | <div class="methodpage-infos"> |
| − | <div class=teaser-box> | + | <noinclude>{{:Navi Before}}</noinclude> |
| − | | |
| − | ===[[Checklist: My learning goals]]===
| |
| − | [[File:check.png | left]]Before leading a group through a learning process,facilittaors can create a list of learning objectives and set a scale next to each skill or ability they would like to improve upon during their moderation.
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| − | | |
| − | </div> | |
| − | <div class="right-column-contentinner">
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Navigation:===
| |
| − | [[File:back.gif | back to the main section]] [[Before]]
| |
| − | *[[The Facilitation Mindset]]
| |
| − | * [[Planning]]
| |
| − | * [[Organizing]]
| |
| | | | |
| | <hr class=simpleline> | | <hr class=simpleline> |
| Line 116: |
Line 55: |
| | *[[Cooperative Learning]] | | *[[Cooperative Learning]] |
| | *[[Management styles]] | | *[[Management styles]] |
| − | *[[Diversity Consciousness]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <hr class=simpleline>
| |
| − | <div class=right-box>
| |
| − | '''Our Handbooks'''
| |
| − | [[File:Holistic-learning-book-cover.png |260px | link=Handbooks for Facilitators]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | E. Heublein, N. Zimmermann
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===Holistic Learning===
| |
| − | Second Handbook for Facilitators: [[Handbooks for Facilitators | Read more]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | </div> | | </div> |