|
|
| (244 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | __NOTOC__
| + | <div class="methodpage-content"> |
| − | [[File:Created-by.png | 20px | Created By ]] [[User:Nils.zimmermann | N. Zimmermann]]
| + | <div class="teaser-text"><div style="background: #eee; float: left; padding: 0px 5px 0px 5px; margin-right: 5px;"><i class="fas fa-arrow-left"> </i> [[Understanding]]</div> [[File:Competences.png | right | 200px |link=https://competendo.net/en/What_Competency-based_learning_is...]]Successful and relevant appli­cation of learning happens when individuals activate and apply knowledge, attitudes and skills in a specific situation. This ability can be described as competence. </div> |
| − | <div class="left-column-contentinner"> | + | |
| − | <div class="teaser-text">[[File:Competences.png | right | 200px]]Successful and relevant application of learning happens when individuals activate and apply knowledge, attitudes and skills in a specific situation. This ability can be described as competence. From a lifelong learning perspective it is a short time people spend in educational institutions. Outside of formal learning settings they continue self-development, gain new insights and shape their personalities. We might conclude, that education and qualification needs to respond to that observation and cover the broad range of experience, attitudes, book-knowledge and skills that one has and needs for his or her active and autonomously shaped life. </div> | + | ==Lifelong Perspective on Education, Learning or Training== |
| | + | From a lifelong learning perspective, it is a short time people spend in educational institutions. Outside of formal learning settings they continue self-development, gain new insights and shape their personalities. This view on learning as a continuous, transformative and diverse process is becoming more important for societies in transitions. |
| | + | |
| | + | Those who see themselves as learners must therefore be particularly competent in reflecting on and articulating their own learning desires and need the ability to learn independently of an accompanying educational structure. Competence-oriented educational programs therefore not only convey content, but also always support the development of these transversal competences. |
| | + | |
| | + | Continous learners are also dependent on educational opportunities that are open at all stages of life. Non-formal education in particular has something to offer here, as it is not tied to formal training paths, can respond to current needs and can therefore also react under conditions of social and demographic change. |
| | | | |
| | <hr class=boldline> | | <hr class=boldline> |
| | | | |
| − | <div style="float: right; font-size: 150px;color: #b4d049; font-weight:bold;">⑩</div> | + | ==Navigate through social changes in a self-determined way== |
| − | ==10 Good Reasons for Competency Based Learning== | + | <div style="float: right; font-size: 140px;color: #1abb83; font-weight:bold;line-height:1.35;"><i class="fas fa-spinner"></i></div> |
| − | Beyond all missionary words we need to acknowledge, that competency based learning is not always easy to implement. It is often a disruptive element in the learning culture of a school, of an academy or an organization. Changes are never easy. In example, in change processes dilemmas appear between old proven and new risky ways of educating. Experience is questioned and new experience was not yet forming. That applies not only to educators or teachers, as well to learners. However, there are very good reasons able to motivate you to try it.
| + | |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="Read more"> | + | Human-centered social change requires individuals feeling capable to address challenges and to co-create a situation in an often ambigous and open context. A transversal understanding of learning is becoming crucial in here, helping learners in mobilising knowledge, skills and attitudes acquired in diverse contexts and social roles. In this perspective the meaning of competence "involves the ability to meet complex demands, by drawing on and mobilizing psychosocial resources (including skills and attitudes) in a particular context" ([http://www.oecd.org/pisa/35070367.pdf OECD]). |
| | + | |
| | + | <div class=left-box> |
| | + | ===Competence (OECD)=== |
| | + | "(Competence) involves the ability to meet complex demands, by drawing on and mobilizing psychosocial resources (including skills and attitudes) in a particular context." ([http://www.oecd.org/pisa/35070367.pdf OECD]) |
| | + | </div> |
| | + | |
| | + | <div class=left-box> |
| | + | ===Key Competences for Lifelong Learning=== |
| | + | "Competences are defined as a combination of knowledge, skills and attitudes, where: |
| | + | * knowledge is composed of the facts and figures, concepts, ideas and theories which are already established and support the understanding of a certain area or subject; |
| | + | * skills are defined as the ability and capacity to carry out processes and use the existing knowledge to achieve results; |
| | + | * attitudes describe the disposition and mind-sets to act or react to ideas, persons or situations." |
| | + | |
| | + | Source: [https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=uriserv:OJ.C_.2018.189.01.0001.01.ENG&toc=OJ:C:2018:189:TOC EU Key Competences for Lifelong Learning] |
| | + | </div> |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | Competence-oriented education is a systematic approach that focuses on the abilities of individuals and aims to strengthen them comprehensively. Learning becomes a partnership between educators and learners and a cooperative social process. The approach combines knowledge, practical skills and attitudes and works closely with real-life challenges. It integrates the training of important transversal skills that are necessary in many social roles and situations. |
| | + | |
| | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="+ Read more" style="float: left;"> |
| | + | <div class=left-box> |
| | + | |
| | + | ===Reasons for Competence-based Learning=== |
| | + | * Considers '''all learners’ experience''' from diverse situations, roles and life phases as relevant. |
| | + | * Goes '''beyond knowledge-centred teaching''', working also on attitudes, values and skills, and reflect how they interplay. |
| | + | * Takes the '''individual learner seriously''' and tailors the learning design to their needs. |
| | + | * Strengthens '''individual ownership''' of their own learning, encourages work on personal competence and the building the ability to learn-to-learn. |
| | + | * Sees learning as a '''social and cooperative process''' – between classroom and real life, formal, non-formal and informal learning, and also between societal sectors. |
| | + | * Appreciates the '''diversity''' of perspectives and learning styles in a group as a potential (instead of trying to even these qualities). |
| | + | * Is '''flexible''', because it understands learning as a non-linear process instead of forcing it into an overly linear curriculum. |
| | + | </div> |
| | + | |
| | + | <div class=left-box> |
| | + | ===What Competence-centered Learning Should Not Be=== |
| | + | *''' A new layer of bureaucracy''': It's intended to give learners and teachers more freedom instead more rules or procedures. It requires flexible teachers/facilitators and more freedom for learners. |
| | + | |
| | + | *'''Tailorist instead tailor-made learning''': It's a humanist and holistic approach aiming to support autonomy, not usability. However, some promoters of competences misunderstand competence-learning as emphasizing on skill training only. |
| | + | *'''Optimization without development''': Competence is not a self-optimization tool nor for assessing the fittest or increasing competitiveness. They are an instrument for individual and free personal development. |
| | + | *'''Doing without thinking''': Competence-centered learning involves knowledge, attitude ''and'' skills. But some understand that it is a practice-only approach. However, successful action is not possible without the ability of a learner to assess and reflect on activities and goals. |
| | + | </div> |
| | + | |
| | <div class=left-box> | | <div class=left-box> |
| − | ===10 Reasons for Competency Based Learning=== | + | [[File: Competence-explorer.png | link= Competence Explorer | right | 120px]] |
| − | * Competency based facilitation gives learners ownership over their learning and is a cooperative social process – '''real and authentic empowerment'''. | + | ===Competence Explorer=== |
| − | * It takes takes '''strengths, needs, and abilities''' of learners for serious. Be more often surprised by the abilities and strengths of your learners.
| + | * Our tool for an overview of different competence frameworks: [[Competence Explorer]] |
| − | * It '''appreciates the diversity''' of perspectives and learning styles in a group as a potential (instead of trying to even these qualities). | + | * Browse the competence models and their definitions |
| − | * Competency based facilitation '''encourages creativity''', because it shapes new connections between topics, people, concepts. | + | * Learn which of these are relevant to your work |
| − | * It stimulates a '''sense of initiative''' and leads to self-efficacy when learners experience a gain of competencies by successful applying their knowledge.
| + | </div> |
| − | * It's '''relevant''', because it allows learners to apply their abilities in a lot of different social roles and situations.
| + | |
| − | *It's more '''flexible''', because it understands learning as a process instead of subordinating it under the regime of a too linear curriculum.
| |
| − | *It allows you to '''focus more on social processes and communication skills''', because competency learning ''is'' a social process.
| |
| − | * You are '''more free from unrealistic learning goals''' or unreal assumptions regarding the needs and abilities of your learners, because mainly the learners abilities are in the focus of competency based learning.
| |
| − | * Thanks to competency based learning you know better, '''how cooperation with different fields of education, social engagement or non-formal education''' increases the quality of education. Because such cooperation allows your learners to apply the learned better under real life conditions.
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | <hr class=boldline> | | <hr class=boldline> |
| | | | |
| − | ===...and 5 Wrong Practices=== | + | ==Democracy and Human Rights-related Learning and Education== |
| | + | Democracy- and human rights-related education and learning approaches that bridge the gap between a systemic understanding of society and the concrete empowerment of learners in a specific (local) context are competence-oriented. |
| | + | |
| | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="+ Read more" data-collapsetext="- Collapse"> |
| | + | |
| | <div class=left-box> | | <div class=left-box> |
| | + | ===Dimensions of Democracy- and Human-rights-related Education=== |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | ====Focus of Democracy-related Learning==== |
| | + | Education encompassing knowledge, action and attitudes is the basis for forms of education such as democracy and human rights education, which aim at the protection of democracy, the empowerment of people as well as at democratic change. Education for democratic citizenship includes learning... |
| | + | * Democracy as a form of '''governance''', including principles, structures and rights. |
| | + | * Democracy as a form of '''living''' and learning, including democratic attitudes and habits. |
| | + | * Democracy as a form of '''society''', including social and participatory processes and relations. |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| − | ===What Competency-centered Learning Should Not Be=== | + | ====Goals of Human Rights Education==== |
| − | *''' Bureaucracy''': It's intended to give learners and teachers more freedom instead more reglementation. It's appreciating the learner and requires flexible teachers or facilitators in supporting them. | + | * Learning '''about human rights''', knowledge about human rights, what they are, and how they are safeguarded or protected; |
| − | *'''Tailoristic''': It's not the modern response to the old education for the workbench but with a similar attitude. Some promoters of competencies misunderstand competency-learning as only emphasizing on skills and skill-gaps. It aims to support autonomy, not usability. | + | * Learning '''through human rights''', recognising that the context and the way human rights learning is organised and imparted has to be consistent with human rights values (e.g. participation, freedom of thought and expression, etc.) and that in human rights education the process of learning is as important as the content of the learning; |
| − | *'''Autonomy terror''': It's not a self-optimization tool for assessing the fittest or making people competitive. Nor is competency-centered education the rationalization of Western ideology. Competencies are neutral – which does not necessarily exclude ideological imprintings of certain competency frameworks.
| + | * Learning '''for human rights''', by developing skills, attitudes and values for the learners to apply human rights values in their lives and to take action, alone or with others, for promoting and defending human rights. |
| − | *'''Stupidity''': Competence-centered learning involves knowledge, attitude ''and'' skills. But that does not support some criticism, that knowledge and reflection of cognitively gained knowledge is less relevant. Competence means even more reflection. All dimensions of experience play a role, need to be strengthend and considered in the methodological concepts. | + | |
| | + | Source: [https://www.coe.int/en/web/compass/introducing-human-rights-education Council of Europe, COMPASS] |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | + | |
| | + | The digital transformation is one example, illustrating how our learning concepts and understanding of education might change toward a holistic perspective. |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | <div class=left-box> |
| | + | |
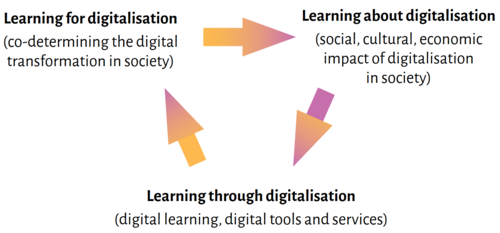
| | + | ===Holistic Digital Transformation Learning=== |
| | + | * Learning '''for''' digitalisation: co-determining the digital transformation in society. |
| | + | * Learning '''about''' digitalisation: social, cultural, economic impact of digitalisation in society. |
| | + | * Learning '''through''' digitalisation: digital learning, digital tools and services. |
| | + | |
| | + | [[File:Tripledigitallearning.png | 500px | center]] |
| | + | |
| | + | </div> |
| | + | |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Line 43: |
Line 118: |
| | <div class=teaser-box> | | <div class=teaser-box> |
| | | | |
| − | ===Competencies=== | + | ===Competences=== |
| − | [[File:Competences1.png | 120px | left]] The focus on applicability of learning, the lifelong perspective and the positive attitude toward learners as the ones being able to co-create their learning biography, these are achievements of competency based learning concepts. A shift has taken place from traditional knowledge dissemination toward modern competency development. | + | [[File:Competences1.png | 120px | left]] The focus on applicability of learning, the lifelong perspective and the positive attitude toward learners as the ones being able to co-create their learning biography, these are achievements of competence-based learning concepts. A shift has taken place from traditional knowledge dissemination toward modern competence development |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="What's inside?"> | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="What's inside?" data-collapsetext="- Collapse"> |
| | + | |
| | + | [[File: Competence-explorer.png | link= Competence Explorer | right | 150px]] |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | <br> |
| | + | ====General Aspects==== |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Competence Frameworks and Non-formal Learning]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Competencies for an Interconnected World]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Competencies for Educators]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Creativity]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Knowledge Society]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Learning to Learn]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Non-Formal Education]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Transversal or Key Competences]] |
| | + | |
| | + | <i class="fa fa-cog"></i> [[Competence Explorer]] |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | ====Democracy- and Human Rights-Related Learning==== |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Civic Competences]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Citizenship Education: Definitions]] |
| | + | |
| | + | <i class="fa fa-cog"></i> [[Card Game: Competences for Democratic Culture]] |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | + | ====Digital Transformation==== |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Digital Competences]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Digital Competences of Educators]] |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | *[[Transversal or Key Competences]]
| |
| − | *[[Knowledge Society]]
| |
| − | *[[Formal, Non-Formal and Informal Education]]
| |
| − | *[[Civic Competences]]
| |
| − | *[[Digital Competences]]
| |
| − | *[[Creativity]]
| |
| − | *[[Competencies for an Interconnected World]]
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| Line 62: |
Line 162: |
| | <div class=teaser-box> | | <div class=teaser-box> |
| | | | |
| − | ===Experiential Learning=== | + | ===Learning Process=== |
| | [[File:Knowledge-society.png | 100px | left]] What we do is the result of observation, action, and reflection. In contrast to a linear understanding of learning, this dynamic could be described as circular development. It involves referring to previous experiences as well as anticipating outcomes, and is fluid. | | [[File:Knowledge-society.png | 100px | left]] What we do is the result of observation, action, and reflection. In contrast to a linear understanding of learning, this dynamic could be described as circular development. It involves referring to previous experiences as well as anticipating outcomes, and is fluid. |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="What's inside?"> | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="What's inside?" data-collapsetext="- Collapse"> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Line 72: |
Line 172: |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Holistic Learning]] |
| − | *[[Holistic Learning]]
| + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Cooperative Learning]] |
| − | *[[Cooperative Learning]]
| + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Facilitation]] |
| − | *[[Self-Directed Learning]]
| + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Directing and Coaching]] |
| − | *[[Emotional Learning]]
| + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Resource Orientation]] |
| − | *[[Creative Thinking]]
| + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Emotional Learning]] |
| − | *[[Divergent and Convergent Thinking]]
| + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Creativity]] |
| − | *[[Non-linear Learning Progress]]
| + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Divergent and Convergent Thinking]] |
| − | *[[Learning Zone Model]]
| + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Non-linear Process]] |
| − | *[[Circular Learning Model]]
| + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Learning to Learn]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Learning Zone]] |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | | | |
| − | <!-- | + | <div class=teaser-box> |
| − | <hr class=boldline> | + | [[File:Empowerment1.png | left | 120px]] |
| | + | |
| | + | ===Power and Participation=== |
| | + | Empowerment in the context of Education for Democratic Citizenship and Human Rights Education has the goal to enable citizens to claim their rights, act in the public, get involved in discussions or decision-making, and live and act according to democratic values. |
| | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="What's inside?"> |
| | | | |
| − | ==Articles==
| |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-expanded" data-expandtext="Read more">
| |
| − | <div class="teaser-box">
| |
| − | ===[[Transversal or Key Competences]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left]] When competences have universal characteristics and are relevant for successful action in very different fields of life, they are named ''transversal'' or ''key'' competences - in contrast to ''specific'' competences which are required more or less only in one specific field or learning context.</div>
| |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="teaser-box">
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===[[Knowledge Society | The Challenge: Knowledge Society]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left]] The idea of a society following the principals of life-long learning started to come into fashion during the 1970’s. In that time the intellectual ideas of reform pedagogy were brought together with an explicit modernist vision of societal development. A crucial role for further development was played by the competency-based style of learning. </div>
| |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="teaser-box"> | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Power]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Empowerment]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Human Rights Education]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Participation]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Facilitation]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Cooperative Learning]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Activism and Participation in Digital Transformation]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Online Participation]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Why do people get involved?]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948)]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[The international Human Rights system after 1948]]<br> |
| | | | |
| − | ===[[Formal, Non-Formal and Informal Education]]===
| + | </div> |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left]] Learning takes place everywhere: in schools, at work, in our spare time, and all throughout our private lives. Educational institutions only specialize in certain aspects of learning. A common understanding is to divide them into three types of educational structures – ones that provide formal, non-formal or informal education.
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | | | |
| | + | <div class=teaser-box> |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="teaser-box"> | + | ===Motivation and Inspiration=== |
| | + | [[File:Motivation.png | 140px | left]]Motivation is vital to self-directed learning, the intrinsic joy in doing well - when we want to achieve something for the resulting personal satisfaction alone. A person’s motivation corresponds to available resources and to his or her own personal needs: The key to intrinsic motivation is the achievement of ''self-actualization''. |
| | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-expandtext="What's inside?"> |
| | | | |
| − | ===[[Civic Competences]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left]] Civic competences enable people to act responsibly in society and in their interaction with other individuals according to values like transparency, openness, social responsibility and human dignity. They are part of a system of transversal (or key) competencies. In contrast to other competences, they refer to shared democratic values which are not self-explanatory.</div>
| |
| − | <div class=teaser-box>
| |
| − | ===[[Digital Competences]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left]]Digital competences describe the ability of people to use information technology and media and and to make sense of it for the personal engagement and development.
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| − | <div class=teaser-box>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===[[Creativity]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left]]Creativity is a core ingredience for becoming able to act proactively as an active citizen, for finding new visions or for fixing concrete problems, for increasing understanding of complex problems and for cooperation with other people or groups. Creativity is a process innate to our brains, one that can be stimulated through facilitation.
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| | | | |
| − | <div class=teaser-box>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===[[Competencies for an Interconnected World]]===
| |
| − | [[File:Article.png | left]]How global, international and European learning contributes to competency development
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| | | | |
| − | </div>
| |
| − | -->
| |
| | | | |
| − | </div> | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[FLOW Model]]<br> |
| − | <div class="right-column-contentinner"> | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Learning Zone Model]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Motivational Style]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Inspiration]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Start with "Why"]]<br> |
| | + | <i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Creative Thinking]] |
| | + | <br><i class="fas fa-glasses"></i> [[Divergent and Convergent Thinking]] |
| | | | |
| − | ===Navigation:===
| + | </div> |
| − | [[File:back.gif | back to the main section]] [[Understanding]]
| + | </div> |
| − | *[[What Competency-based learning is... ]]
| |
| − | * [[Empowerment]]
| |
| − | *[[Group-related and Interpersonal Aspects]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | <!-- | + | |
| − | **[[Transversal or Key Competences]]
| + | <!-- |
| − | **[[Knowledge Society]]
| + | <hr class=boldline> |
| − | **[[Formal, Non-Formal and Informal Education]]
| + | ===Tool:=== |
| − | **[[Civic Competences]]
| + | [[File: Competence-navigator-logo.png | 200px | center | link= Competence Navigator]] |
| − | **[[Digital Competences]]
| |
| − | **[[Creativity]]
| |
| − | **[[Competencies for an Interconnected World]]
| |
| | --> | | --> |
| − | <hr class="simpleline"> | + | <hr class=boldline> |
| | | | |
| − | <div class="right-box" >
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | ===DEFINITION:=== | + | <div class=teaser-box> |
| − | [[File:Knowledge-society.png | 150px | center | A competency is more than just knowledge and skills. It involves the ability to meet complex demands.]]<br>"A com­pe­tency is more than just know­ledge and skills. It involves the ability to meet complex demands, by drawing on and mobili­zing psycho­social resources (including skills and attitudes) in a particular context."
| + | |
| − | [http://www.oecd.org/pisa/35070367.pdf OECD]
| + | ==Competence Frameworks that Address Learners== |
| | + | Materials from the community |
| | + | <noinclude>{{:Resources - Competence Frameworks}}</noinclude> |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | + | <hr class=boldline> |
| | | | |
| − | <hr class="simpleline"> | + | <div class=teaser-box> |
| | | | |
| − | ===Related:=== | + | ==Competence Frameworks for Educators== |
| − | *[[Planning with Key Competencies]]
| + | Materials from the community |
| − | *[[Key Competency Profile]]
| + | <noinclude>{{:Resources - Competence Frameworks For Educators}}</noinclude> |
| − | *[[Method Mix]]
| + | </div> |
| − | *[[Describing Competency Development]]
| |
| | | | |
| | + | </div> |
| | + | <div class="methodpage-infos"> |
| | + | <noinclude>{{:Navi: Understanding}}</noinclude> |
| | | | |
| | + | <hr class=simple-line> |
| | + | <div class="left-box" > |
| | + | ===DEFINITION:=== |
| | + | [[File:Knowledge-society.png | 250px | center | A competence is more than just knowledge and skills. It involves the ability to meet complex demands.]]<br>"A com­pe­tence is more than just know­ledge and skills. It involves the ability to meet complex demands, by drawing on and mobili­zing psycho­social resources (including skills and attitudes) in a particular context." |
| | + | [http://www.oecd.org/pisa/35070367.pdf OECD] |
| | + | </div> |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − |
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |