 N. Zimmermann/ H. Fahrun
N. Zimmermann/ H. Fahrun
Evaluation is the structured interpretation and giving of meaning to predicted or actual impacts of proposals or results. It looks at original objectives, and at what is either predicted or what was accomplished and how it was accomplished. So evaluation can be
formative, that is taking place during the development of a concept or during a seminar, with the intention of improving the value or effectiveness of the proposal of the project. It can also be
assumptive, drawing lessons from a completed action of the project or a finished seminar.
Focuses of reflection
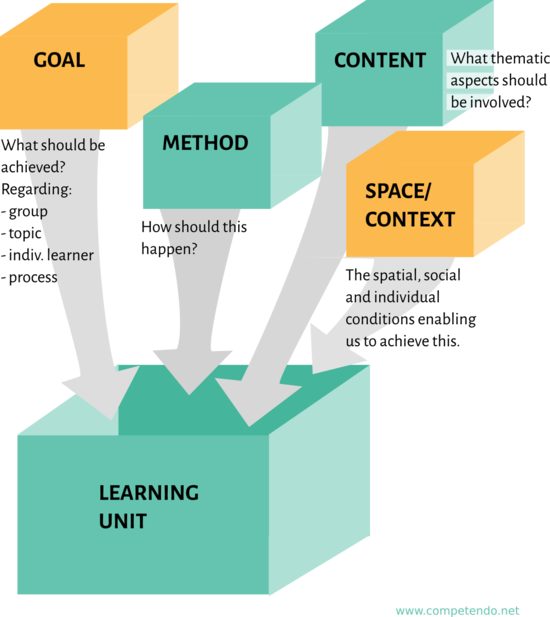
During Planning faciliators were considering goals, contents, methods, topic, needs and the environment. From time to time it's needed to check if the process is still inline with the plans or if priorities have changed needs are different, or a process should take a general different direction.
Goal Achievement
- Group: Regarding the aimed interaction and cooperative learning in the group
- Topic: The coverage of the foreseen topical aspects
- Individual: Learning/development goals (in particular competency development, see below)
- Process: The proceeding of the collective learning process
|
Methodology
- The choice of methods and their mix
- The ability of facilitators to implement their methodological concept
- Process moderation
|
Content
- Coverage of the necessary thematical aspects in a satisfactory deepness
- Inclusion of knowledge from the field participation/citizenship/democracy and how it was connected to the goal of the training
|
Space/Context
- Facility: Opportunity to learn, to cooperate, to meet, to feel well accommodated
- Group: Opportunity and ability to involve, interact, relate to the other learners
- Individual needs: Possibility to satisfy individual needs inside and outside the scheduled activities: social, cultural/spiritual, physical, intellectual, emotional
- With special attention to special needs
- Inclusion of the local environment: in seminar work, in topical aspects
|
Competency development
- Participant's acquisition of competencies
- Participant's development towards feeling self-empowered and their ability to democratic participation
- Your acquisition of competencies as a facilitator
|
Management
- Event management, logistics, problem-solving
- Cooperation within the facilitation team
|
Concept: The Method Mix
The quality of results depends from the methodology how the data for reflection was collected. In particular a range of different ways to assess and interpret the needed data should be included, according to the principle of method mix.
Method Mix:
Style
- Choose appropriate methods for your target group
Confidentiality:
- Anonymous, half-public, or public
Group Relation
- In a plenum, in other collaborative ways, or in individual work
Addresses different senses
- Individually speaking, dialogue, writing, or moving
Quantitative or qualitative?
How deep should or needs your evaluation go? When you want to know how your participants feel, you ask them to show you “thumb up/down”. Afterwards you know that ten persons feel well and three of them not so well. Or you ask detailed qualitative questions, with which you find out why they feel themselves like that or what they need to feel better. You use a quantitative and a qualitative method – both of them are all right, when they suit the situation, they often complement each other.
Documentation of the Results
Choosing your method you should also consider the form, in which you need results. Language, pictures, photos… Many things are possible and they can complete a particular situation or also contrast it. It is important with most methods to formulate a question as concretely as possible.
As self-evaluation is crucial for independent learning, we include here as well methods, that help individuals to document learning outcomes, inspirations, insights in and individual way.
Selected Methods: Individual Reflection and Assessment
An overview over different methods for evaluation for evaluation in between and at the end of a learning process.
Ask participants to visualize their back activities like a project or the activity within a longer learning process. The vizualition will be made in form of a learning curve. The horizontal axis describes time, the vertical axis describes the feeling associated with the activity/project and the learning outcome.
Participants of a training or seminar document the aspects of a meeting that are most essential for their future activities. They remember these aspects and gain motivation after the meeting.
The method combines evaluation of the past activities with the future perspectives and the opportunities zhat appear through the gain of competences as a result of project work.
Portfolios help the participants to reflect on their way of learning and on Sustainable Development on a personal level. No one is going to look at it – it’s a personal (structured) diary. It will accompany the participant through their whole activity.
Bullet journalling is a creative methodology how to strucuture notes and thoughts, how to save thoughts and inspiration. Helpful for facilitators as for participants, in example in learning journals or their notes.
The activity aims at evaluating the outcomes that the projects have had on the community as well as to enabling the participants to evaluate these outcomes from different perspectives.
Selected Methods for Group Evaluation
These methods are facilitating a collective process of reasoning. Therefore, they are less confidential, allowing the group to exchange or discuss their observations or findings.
With this method you can determine in a group which subjects you want to deal with and which project goal is for you crucial. Or you can identify the most important aspects of further planning in the team. You can also gather what you like in the subject, which organizational or regarding the contents aspects of the project were most interesting.
With this method many different aspects can be quickly evaluated within a group in a transparent way.
This method aims at letting the participants conduct a small-scale survey among each other, having a vivid visual representation of the survey outcome and facilitating a discussion around the survey outcome.
Reflect on conflicts you had in your team and learn from it for future work.
The color diary is a creative tool which can be used for evaluation of the day throughout the training.
This activity stimulates creative reflection on the working process and can be easily adopted to reflect on or discuss any given topic.
Feedback is a method that was developed to improve the quality of interpersonal communication, in terms of relevance (giving relevant information) as well of moral quality (showing interpersonal respect). It is a skill that has to be improved upon and includes often very useful information. In order to gain from this information people need to develop the capacities to give and receive feedback.
This activity can be used during the last day of the training to create a lasting bond during the participants.
Self-Assessment of Facilitators
Checklists for a team of educators or for individual self-assessment.
Here you can find a self-assessment checklist for facilitators.
A team of facilitators is diverse in terms of their preferences and working style. This checklist helps you to reflect your working style and to talk in your team about your personal preferences.
A team of facilitators is diverse in terms of their preferences and working style. This checklist helps you to reflect your working style and to talk in your team about your personal preferences.
Navigation:
 After
After
Example: Aquarium
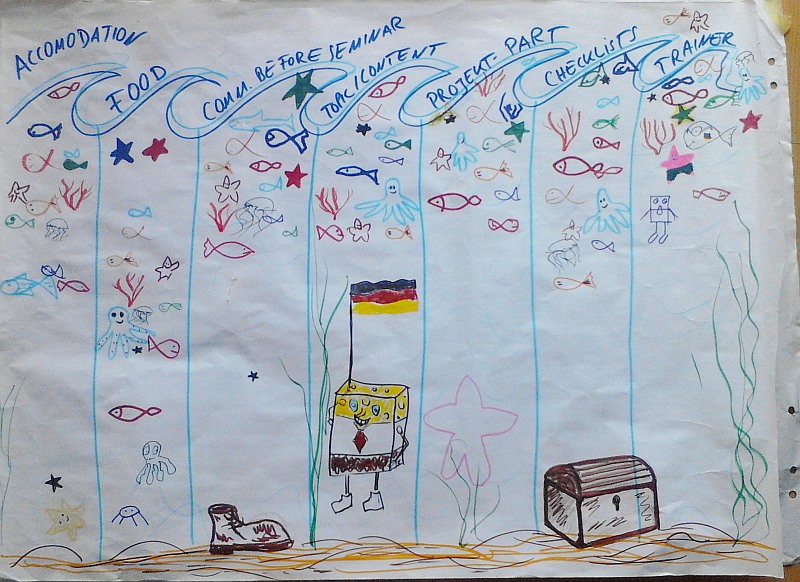 A cooperative evaluation in a training. Each participant marks his or her fish. Near the surface means +, at the ground means -.
A cooperative evaluation in a training. Each participant marks his or her fish. Near the surface means +, at the ground means -.
Evaluation is the structured interpretation and giving of meaning to predicted or actual impacts of proposals or results.
Our Handbooks

E. Heublein, N. Zimmermann
Holistic Learning
Second Handbook for Facilitators: Read more
![]() N. Zimmermann/ H. Fahrun
N. Zimmermann/ H. Fahrun
 A cooperative evaluation in a training. Each participant marks his or her fish. Near the surface means +, at the ground means -.
A cooperative evaluation in a training. Each participant marks his or her fish. Near the surface means +, at the ground means -.